When creating a new mailbox for a user Jim Murphy, the shell command used is displayed in the screenshot below.
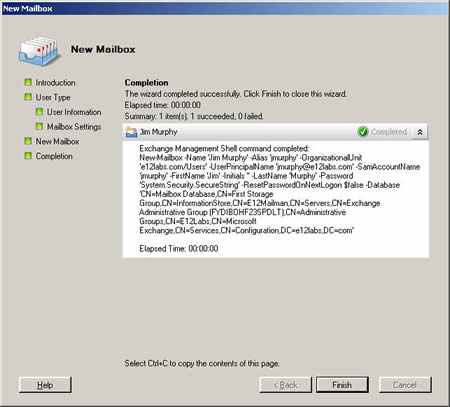
Parameters used by the command displayed in the above screenshot:
1) Name: Jim Murphy
2) Alias: jmurphy
3) OrganizationalUnit: e12labs.com/users (Domain/Container or OU)
4) sAMAccountName: jmurphy
5) FirstName: Jim
6) Initials: '' (blank)
7) LastName: Murphy
8) Password: System.Security.Secure.String (hidden)
9) ResetPasswordOnNextLogon: $false
10) Database: distinguishedName of the mailbox database
The new-mailbox command creates a new user account in Active Directory, and a new mailbox in Exchange. Documentation for the new-mailbox command has an extensive list of all the parameters - required and optional.
However, a new mailbox can be created using far fewer parameters - as shown below:
$password = Read-Host "Enter Password" -AsSecureString
The new-mailbox command does not accept a password if it is actually typed inline in the command, e.g. new-mailbox -password MyPassw0rd1.... The command in the above example results in the shell providing a prompt to securely enter a password, without making it visible in the shell. It is held in the variable $password. The variable can then be used in the new-mailbox command.
New-Mailbox -Password $password -Name "Jim Murphy" -UserPrincipalName [email protected] -OrganizationalUnit Users -Database "Mailbox Database"
Note, not all the parameters used and displayed by the New Mailbox wizard are required. Some parameters, like alias are populated automatically by the shell. You can use the get-mailbox command to list all parameters for a mailbox, and determine which parameters were populated automatically.get-mailbox "Jim Murphy" | fl
Labels: Exchange Server 2007, Exchange Shell, Mailbox
 Exchangepedia Blog is read by visitors from all 50 US States and 150 countries world-wide
Exchangepedia Blog is read by visitors from all 50 US States and 150 countries world-wide



0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Links to this post:
Create a Link
<< Home